Pages
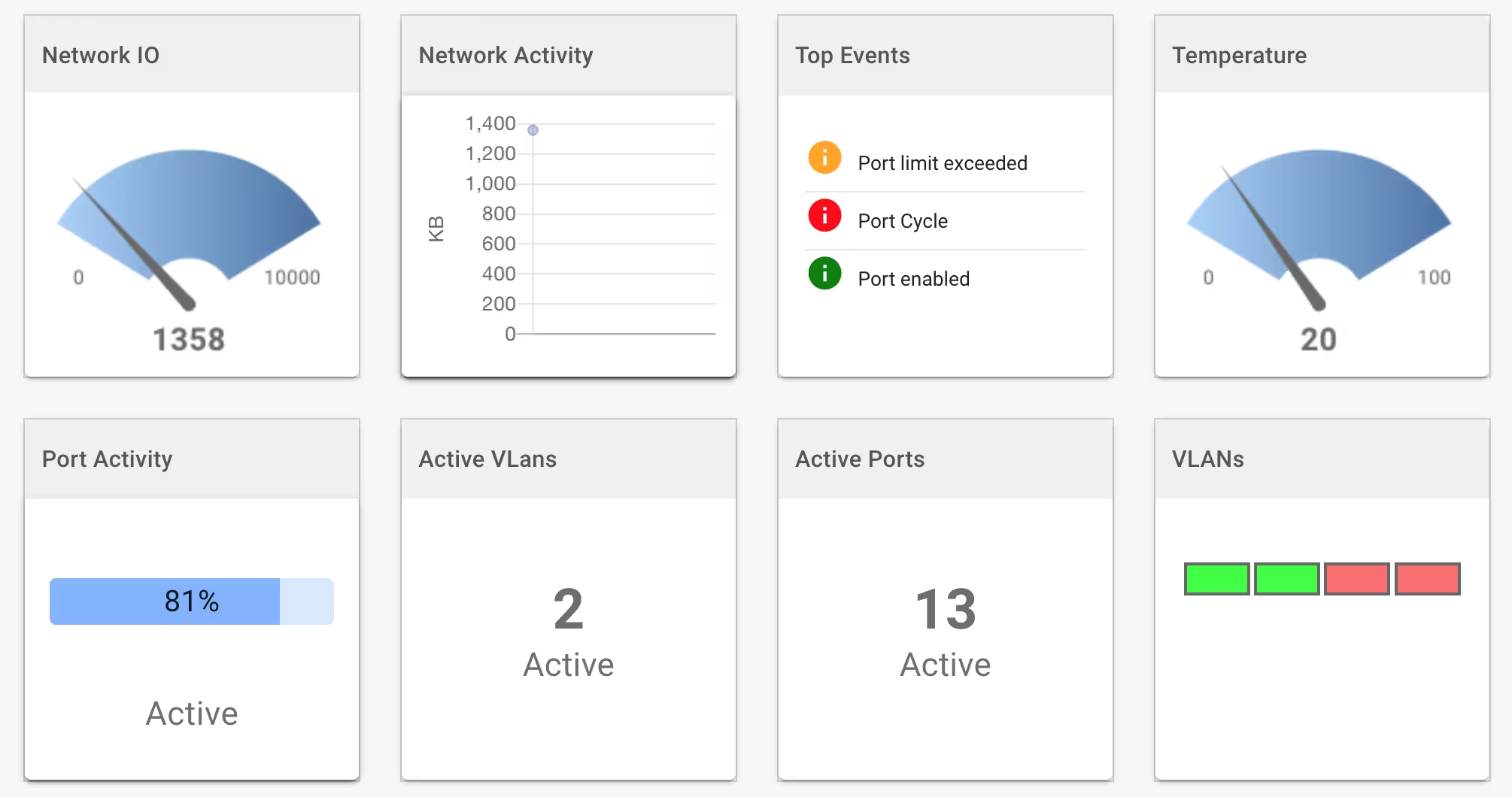
The DevCore framework enables you to create custom UI pages for different aspects of device operation and performance. You can build focused interfaces for specific functions, such as control panels for key device parameters, performance dashboards with service load graphs and metrics, or diagnostic pages for monitoring outages and errors.
Pages are created using drag-and-drop functionality to arrange widgets on a canvas. They can be styled with CSS properties, including background colors or images, to create professional interfaces tailored to your device management needs.
You can also create pages that utilize custom UI components of your own design.
Page Architecture
The Page Designer utilizes the DevCore framework's Board component, which provides the foundation for both pages and dashboards. This component offers:
- Widget Management - Comprehensive widget library for data display and user input
- Layout Systems - Flexible positioning and sizing options
- Responsive Design - Automatic adaptation to different screen sizes
- Styling Control - CSS-based customization capabilities
For detailed information about the underlying components, see:
Page Features
The DevCore framework provides comprehensive tools for creating device management interfaces. You can create pages and configure how they are integrated into the app. For each page you can configure:
- Page Navigation - The page navigation URL and menu items
- Page Title - The title displayed at the top of the page
- Page Component - The VueJS component used to render the page
- Page Order - The display order in relevant app menus
- Page Authentication - The required user role to access the page
- Page Content - The page content and layout
Page Management
From the Pages list you can add or modify pages. Add a page by clicking the Add button. Click the edit icon to modify an existing page.
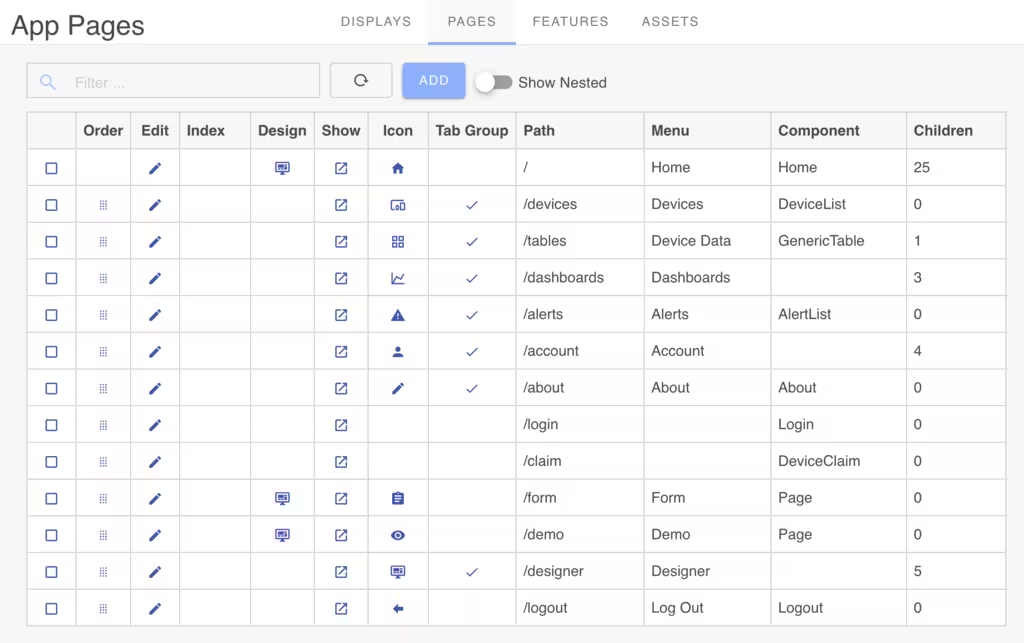
After creating a page, access the Page Designer by clicking the Design icon in the pages list. Only pages that use the Page component will have a Design icon. Other pages have fixed layouts and contents and cannot be edited via the Page Designer.
Page Order
You can configure the page order by dragging and dropping pages in the list. The page order defines the sequence in the app sidebar menu or tabbed menus.
Creating and Editing Pages
When adding or editing a page, the page properties panel will be displayed.
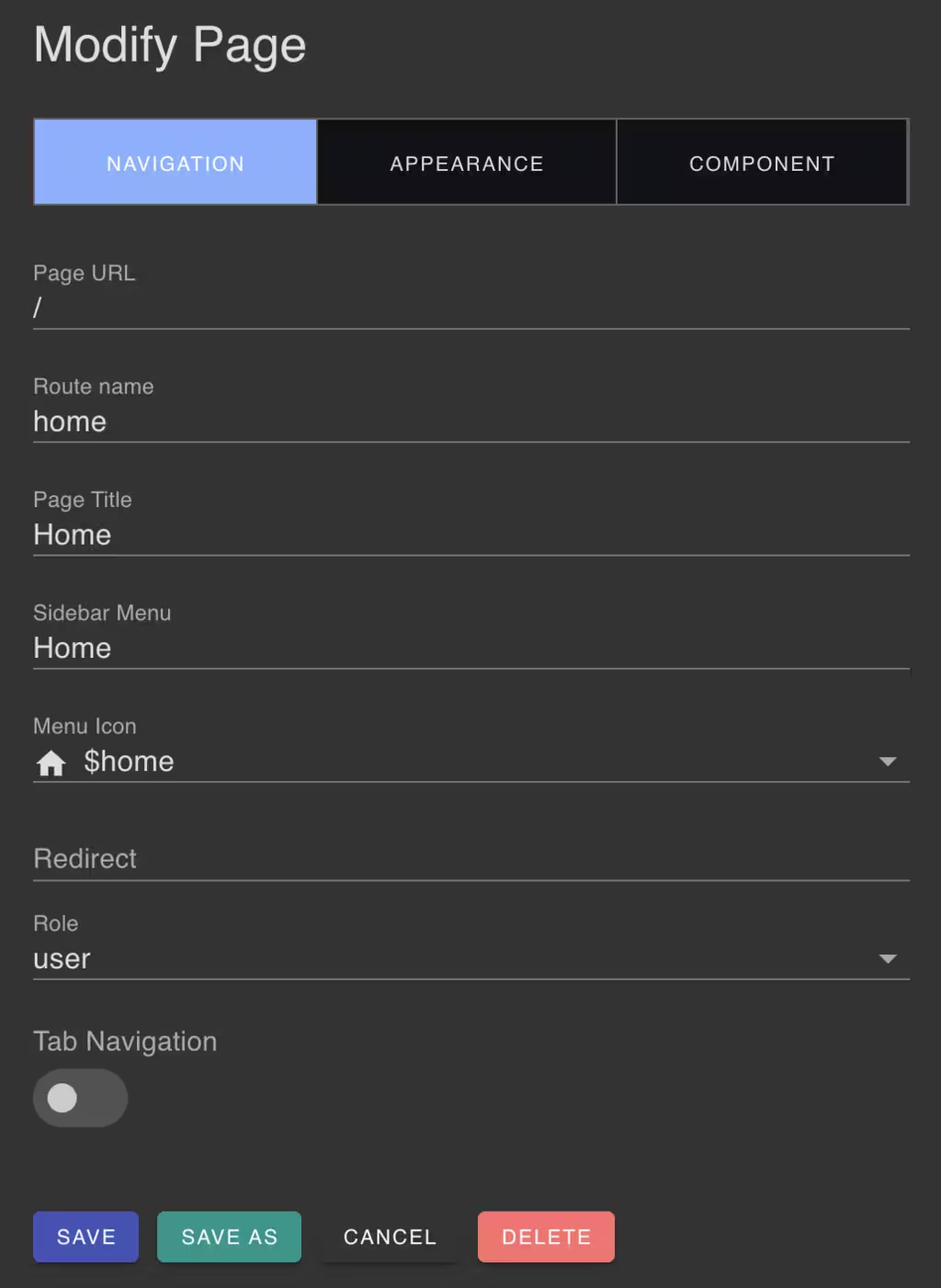
Page Navigation
Under the Page Navigation section you can configure the page navigation URL and menu items. The page navigation URL is the URL that will be used to access the page. The menu items are the items that will be displayed in the app sidebar menu. You can configure the page menu icon and user access role.
The page title is the title that will be displayed at the top of the page.
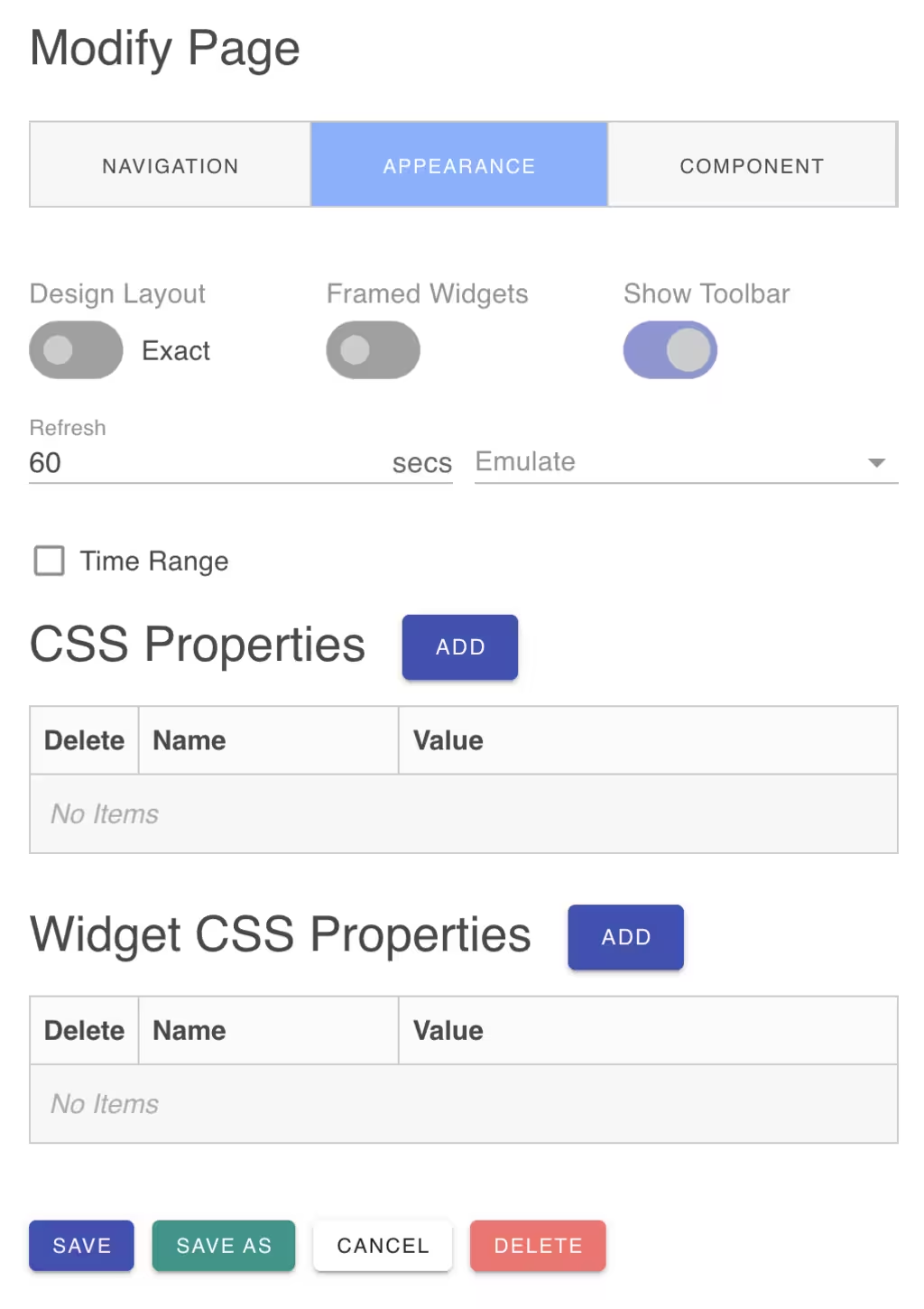
Page Appearance
For pages that use the Page component, you can configure the page appearance:
- Design Layout - Set the design-time page layout to
GridorExact. The Grid layout is the default and snaps widgets to a 20-pixel grid. The Exact layout allows you to position widgets with exact coordinates. - Frame Widgets - Enable or disable widget frames. Frame widgets display a border around the widgets.
- Toolbar - Enable or disable the page toolbar. The toolbar displays the page title and action buttons at runtime.
- CSS Properties - Set page colors, fonts, borders and more using CSS properties.
- Widget CSS Properties - Set common properties to be inherited by all widgets.
Page Component
The Page Component tab configures the VueJS component used to render the page and the component properties. The Page component is the default component that supports the Page Designer and widgets.
Page Designer
After creating a page, access the Page Designer by clicking the Design icon in the pages list.
When the Page Designer is launched, you will see the page canvas with the page title and toolbar. To the left is the widget toolbox.
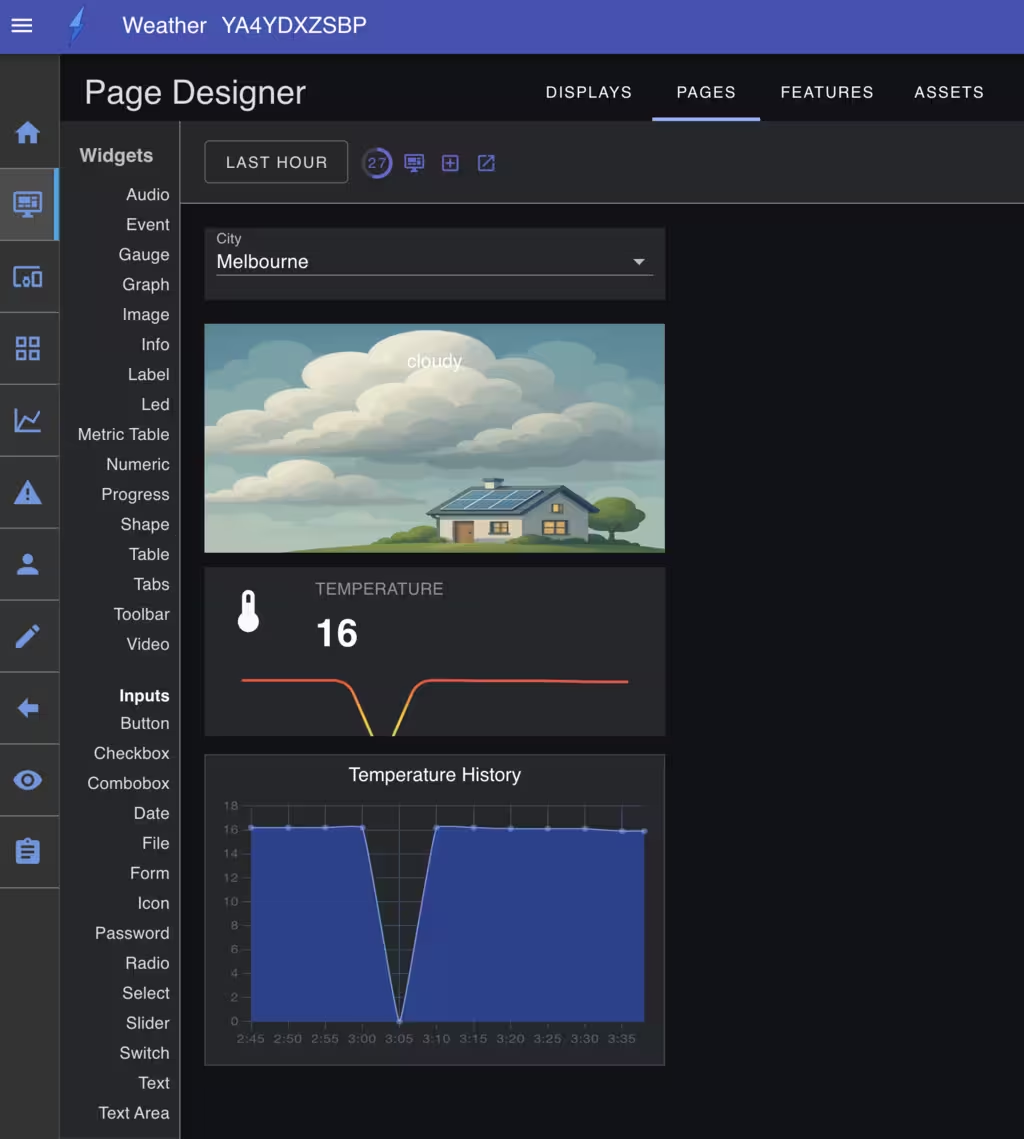
Page Canvas
The page canvas is the main area where you can design the page layout and content. It is where you can add and position widgets, and it scales according to the screen size.
The page canvas uses percentage-based sizing and positioning of widgets. As the window is scaled or resized, the widgets will resize to maintain the same relative width and will adjust their position to occupy the same relative position. This offers automatic scaling and consistent presentation across different devices and screen sizes.
Note that you can always use the multiple-display capability if you have specific device requirements that cannot be met by responsive design.
When placing and configuring widgets, you can drag them to the desired position and size on the canvas. You can also anchor widgets to a specific position relative to the canvas edges. This is useful to create fixed position elements like page titles or footers.
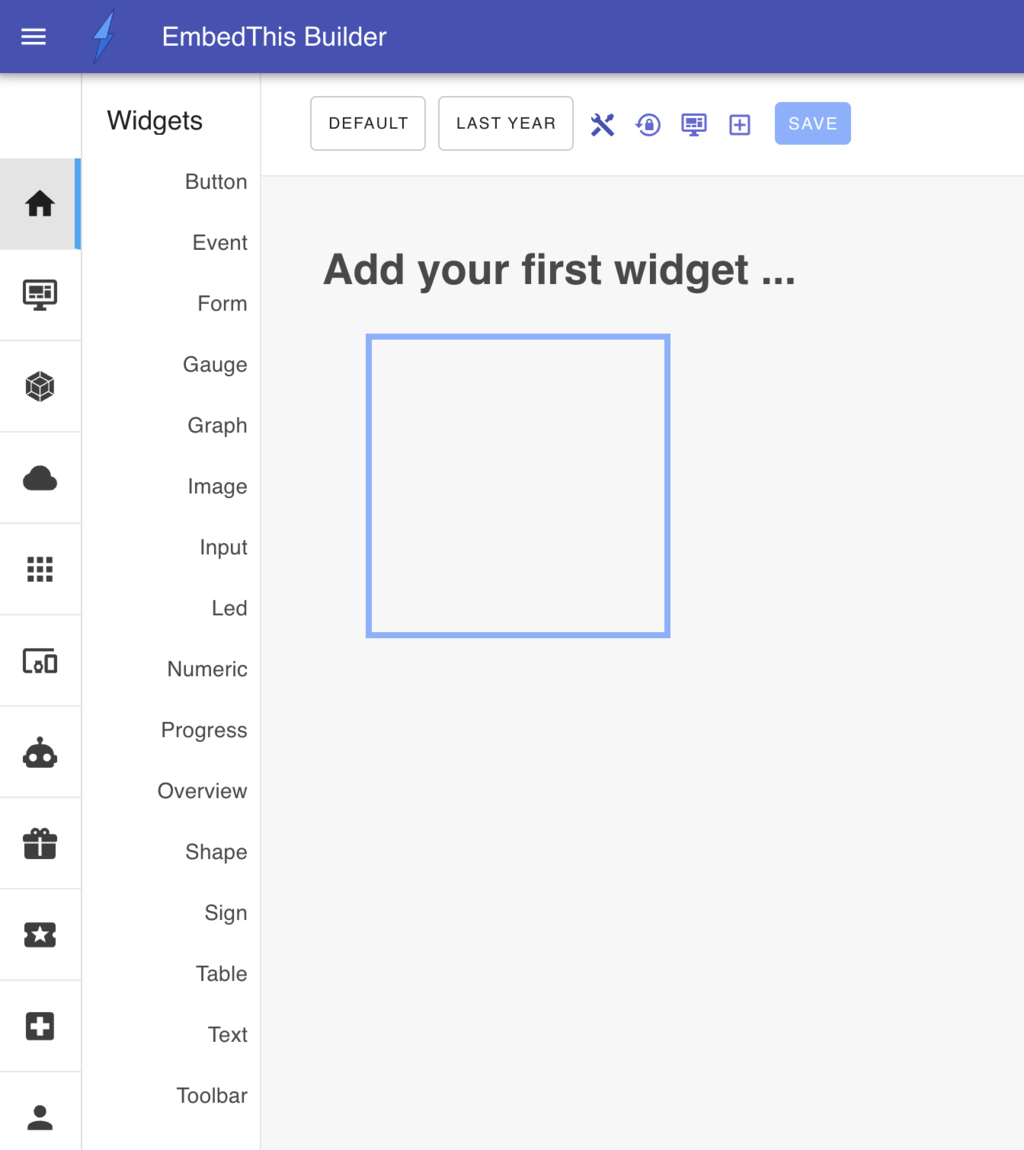
Adding Widgets
You can add widgets to the page canvas in two ways:
- Drag and Drop - Drag widgets directly from the widget toolbox onto the page canvas
- Add Widget Panel - Click the
Add Widgetplus icon in the page toolbar (second icon from the right)
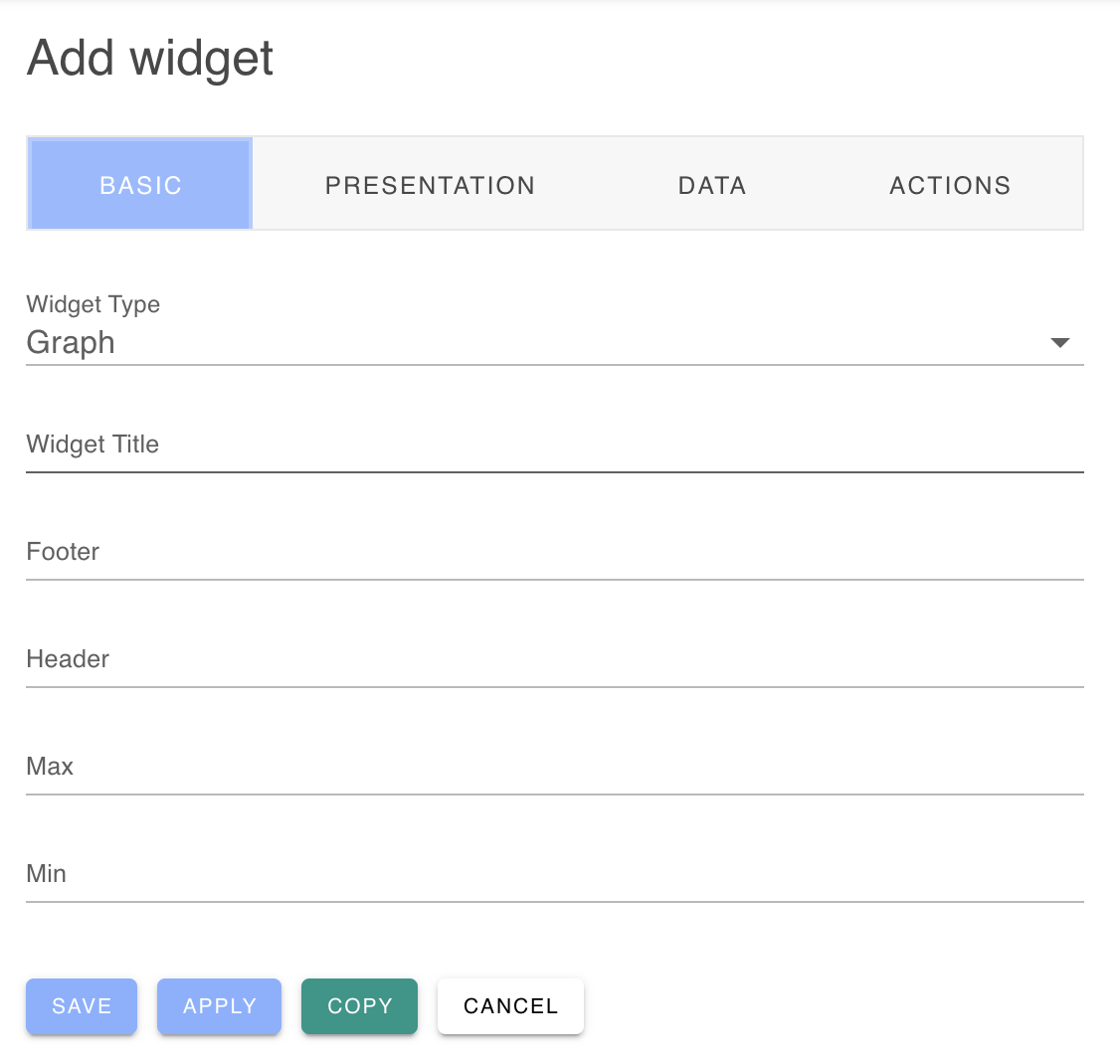
When first adding a widget, the widget configuration panel will be displayed so you can define or modify the widget properties:
- Widget Type - Select the appropriate widget for your data
- Widget Presentation - Customize the widget appearance and style
- Data Source - Connect the widget to real-time or historical metrics or device data
- Actions - Configure cloud-side user actions in response to user interaction
Widget Library
The widget toolbox contains a library of widgets that you can add to the page canvas. The widget library is organized into categories:
Output Widgets
- Graphs, gauges, numeric displays, text, images, event indicators, data tables
Input Widgets
- Buttons, checkboxes, comboboxes, select lists, date pickers, file inputs, sliders, switches, text areas, radio buttons
See the Widgets page for more information about the widgets available. See the Input Widgets page for more information about the input widgets available. See the Output Widgets page for more information about the output widgets available.
Widget Layout
The Page Designer supports two design-time layout engines:
Grid Layout
- Automatic Alignment - Widgets snap to a 20-pixel grid
- No Overlap - Prevents widgets from overlapping
- Easier Positioning - Simplified widget arrangement
- Recommended for Beginners - More intuitive for new users
Exact Layout
- Pixel-Perfect Positioning - Place widgets with exact coordinates
- Overlap Support - Widgets can overlap and layer
- Composite Interfaces - Create seamless, integrated UI pages
- Advanced Control - Full control over widget positioning
Design Workflow
When creating pages, it is recommended to use the Grid layout and the Framed option for your initial design. This will make it easier to position and arrange widgets. When you have your rough design complete, you can switch to Exact layout without frames for the final presentation. The Exact layout is useful to create pixel-perfect interfaces and permits widgets to overlap and layer.
Best Practices
Design Workflow
- Plan Layout - Sketch page structure before building
- Start with Grid - Use grid layout for initial widget placement
- Use Framed Mode - Enable widget frames during design
- Test Responsiveness - Check behavior across different screen sizes
- Optimize for Target - Switch to exact layout for pixel-perfect control if needed
Widget Organization
- Group Related Widgets - Arrange functionally related elements together
- Consider Information Hierarchy - Place important information prominently
- Maintain Consistency - Use consistent styling across widgets
- Plan for Mobile - Consider mobile viewing experience
Performance Considerations
- Limit Widget Count - Too many widgets can impact performance
- Optimize Data Sources - Ensure efficient data connections
- Test with Real Data - Verify performance with actual device data
- Monitor Resource Usage - Check memory and CPU impact
Page Configuration
- Use Appropriate Layout - Choose Grid for ease of use, Exact for precision
- Consider User Roles - Set appropriate authentication requirements
- Test Navigation - Verify menu integration and URL routing
- Optimize for Purpose - Tailor page features to intended use case
